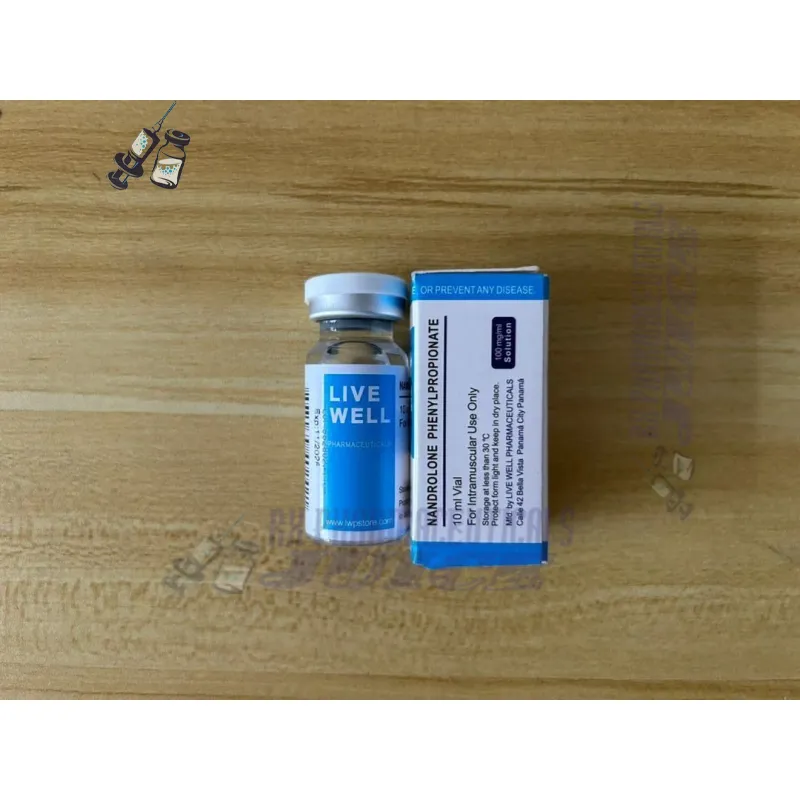
Description for Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP 100mg)
Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP) is a synthetic anabolic androgenic steroid (AAS) that is derived from the hormone testosterone. It is part of the larger family of Nandrolone compounds, which also includes Nandrolone Decanoate (Deca Durabolin). NPP is known for its powerful muscle-building and performance-enhancing properties, making it a popular choice among bodybuilders and athletes.
NPP was first developed in the 1950s and has since gained significant attention in the world of sports and fitness. It is commonly used for its ability to promote muscle growth, increase strength, and enhance athletic performance. In medical settings, NPP is also used to treat conditions such as anemia, osteoporosis, and muscle wasting diseases.
The chemical structure of NPP is similar to that of testosterone, with a modification in its ester chain. This modification gives NPP a shorter half-life compared to Nandrolone Decanoate, resulting in faster clearance from the body. As a result, NPP requires more frequent administration, typically with injections every other day or every three days.
NPP works by binding to androgen receptors in the body, promoting protein synthesis and nitrogen retention in muscle tissues. This leads to an increase in muscle mass and strength. Additionally, NPP has a mild estrogenic effect, which can help with joint lubrication and alleviate joint pain commonly associated with intense workouts. These properties make NPP a favorable choice for athletes and bodybuilders looking to improve their performance and physique.
When using NPP, it is important to note that it can have both positive and negative side effects. Some of the positive effects include increased muscle mass, enhanced recovery, improved endurance, and increased red blood cell production. However, like any other AAS, NPP also carries the risk of potential side effects.
One of the most common side effects of NPP is androgenic in nature. This means that it can cause the development of masculine characteristics in both men and women, such as increased facial and body hair, deepening of the voice, and acne. In women, it can also lead to menstrual irregularities and clitoral enlargement.
NPP also has the potential to suppress natural testosterone production in the body. This can result in a decrease in libido, erectile dysfunction, and mood swings. To mitigate this, many users include a testosterone base in their NPP cycles to maintain normal hormonal balance.
Liver toxicity is another concern when using NPP, although it is generally considered to be milder compared to other AAS. However, it is still important to monitor liver function while using NPP, especially when using high doses or for prolonged periods.
As with any AAS, the misuse and abuse of NPP can have serious health consequences. It is important to follow recommended dosages and cycle lengths to minimize the risk of side effects. Additionally, it is crucial to undergo regular medical check-ups to monitor overall health and to discontinue use if any negative symptoms arise.
In conclusion, Nandrolone phenylpropionate (NPP) is a synthetic anabolic androgenic steroid with potent muscle-building and performance-enhancing properties. It is widely used by athletes and bodybuilders to increase muscle mass, strength, and athletic performance. However, it is important to use NPP responsibly and with caution, as it can have both positive and negative effects on the body. Proper dosage, monitoring, and adherence to cycle lengths are crucial to minimize potential side effects and maintain overall health and well-being.